SQL monitoring is the process of tracking and analyzing the health, performance, and efficiency of SQL databases. It ensures that database queries execute optimally, resources are utilized efficiently, and potential bottlenecks are detected and resolved before they affect application performance. SQL monitoring plays a crucial role in database administration, helping teams maintain high availability, minimize downtime, and enhance overall database reliability.
In this article, we will take a look at SQL monitoring— key components, how SQL monitoring works, and how to choose the right tool.
Understanding how your SQL queries behave is fundamental to optimization. By diligently monitoring query performance, you can pinpoint bottlenecks and inefficiencies. Analyzing execution plans—the database's roadmap for processing your query—along with indexing strategies and query structure empowers administrators to:
Effectively monitoring resource utilization is crucial for maintaining a balanced SQL database. By observing resource utilization patterns, you can detect potential contention issues that might hinder performance.
For instance, consistently high CPU usage, memory pressure, or disk bottlenecks often signal underlying problems, such as inefficient queries or suboptimal database configurations, providing valuable insights for optimization.
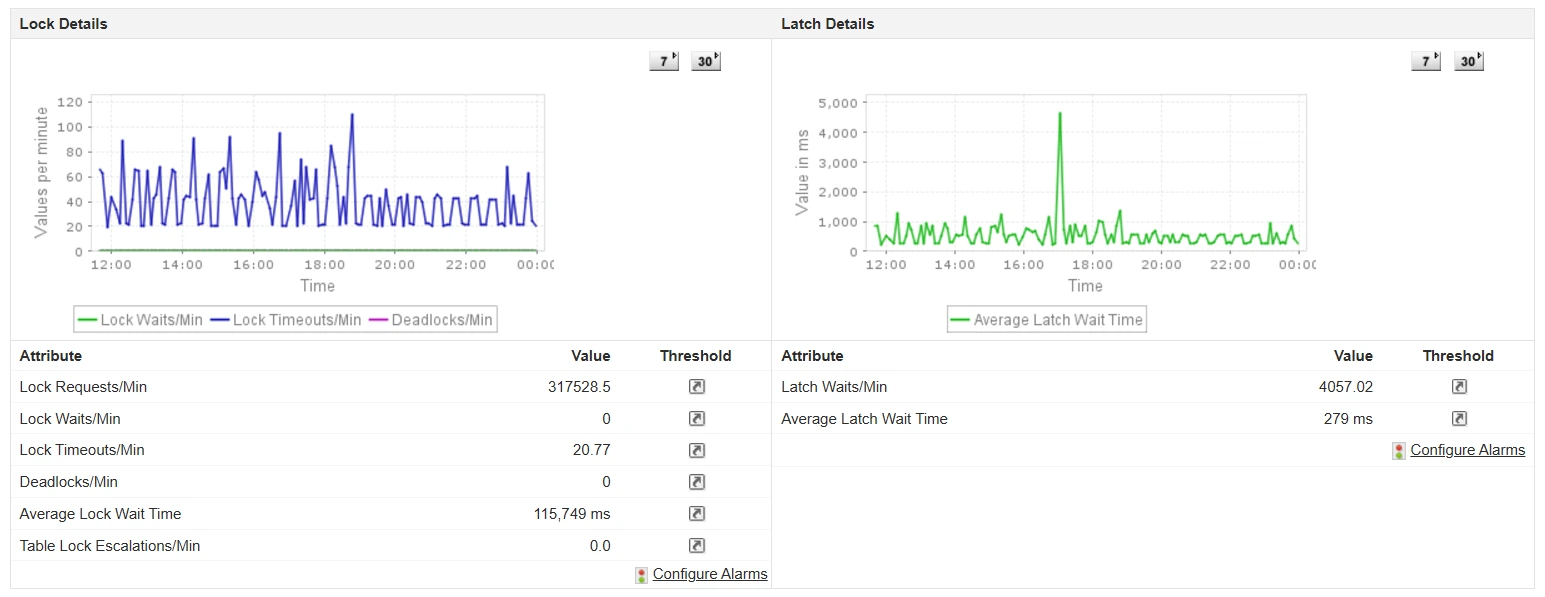
Locking is essential for maintaining data integrity in SQL databases. However, excessive locking or deadlocks can lead to significant performance problems. Monitoring locking behavior is crucial for preventing contention and deadlocks in SQL transactions.
By identifying transactions that hold locks for extended periods or block other processes, you can:
TempDB serves as a workspace for temporary storage and intermediate query processing. If TempDB runs of disk space, any SQL Server activity requiring its use will be halted, leading to query failures and blocking of other operations. Features that rely on TempDB's version store, such as Read-Committed Snapshot Isolation (RCSI), snapshot isolation, online index operations, and AFTER triggers, may also fail or function incorrectly if TempDB is full.
Transaction logs record every change made to the database. If transaction log growth is not monitored and managed, it can lead to severe consequences:
Indexes enable rapid data retrieval, but their effectiveness can diminish over time due to fragmentation. High fragmentation levels can significantly impact performance, necessitating index reorganization or rebuilding to restore efficiency.
Regular index monitoring and fragmentation analysis are essential for maintaining optimal query execution. It can also help with identifying unused or duplicate indexes that consume unnecessary resources. Its important to monitor buffer cache as well to ensure efficient data retrieval.
Analyzing wait statistics allows you to identify the primary sources of delays in SQL query execution, such as CPU waits, I/O waits, or network latency. SQL databases track wait events, which provide invaluable insights into performance bottlenecks. This data empowers administrators to fine-tune database configurations and address the root causes of performance issues, leading to significant improvements in overall efficiency.
Monitoring replication status, latency, and failover readiness is crucial for ensuring that secondary instances remain synchronized and can seamlessly take over in the event of a primary database failure. Many SQL environments leverage replication, clustering, or failover setups for high availability and disaster recovery. This vigilant monitoring guarantees business continuity and minimizes downtime.
Tracking user activity, access patterns, and potential security threats, such as SQL injection attacks, is essential for safeguarding sensitive data. SQL monitoring extends beyond performance optimization to encompass security and compliance. Compliance monitoring ensures that databases adhere to industry regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS, maintaining data integrity and protecting against legal and financial risks.
Monitoring backup success rates, backup frequency, and restore validation is crucial for ensuring that data can be recovered quickly and reliably in the event of failures or data corruption. Database backups are the lifeline of any SQL environment, providing a safety net against data loss. Regular testing of restore procedures further reinforces this safety net, providing peace of mind and ensuring business resilience.
Selecting the right SQL monitoring solution depends on several factors, including:
SQL monitoring is essential for maintaining efficient, reliable, and high-performing database systems. By continuously tracking query execution, resource usage, security events, and replication status, organizations can ensure optimal database performance and prevent costly downtime.
ManageEngine Applications Manager enables real-time monitoring of SQL server, offering deep insights into database health, query performance, and resource consumption.
 It helps diagnose slow queries, enhance efficiency, and prevent performance issues with proactive alerts. AI-powered notifications ensure smooth database operations, while detailed reports provide valuable insights for strategic optimization. Applications Manager also offers application monitoring, infrastructure monitoring and digital experience monitoring capabilities alongside SQL monitoring.
It helps diagnose slow queries, enhance efficiency, and prevent performance issues with proactive alerts. AI-powered notifications ensure smooth database operations, while detailed reports provide valuable insights for strategic optimization. Applications Manager also offers application monitoring, infrastructure monitoring and digital experience monitoring capabilities alongside SQL monitoring.
Try a 30-day, free trial of Applications Manager now!

It allows us to track crucial metrics such as response times, resource utilization, error rates, and transaction performance. The real-time monitoring alerts promptly notify us of any issues or anomalies, enabling us to take immediate action.
Reviewer Role: Research and Development
Trusted by over 6000+ businesses globally